How Does Activity Explain the Differences in the Observed Solubility
It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a solvent at. For organic liquids both real and hypothetical ones the.
6 9 Activity Effects Chemistry Libretexts
As water molecules heat up they vibrate more quickly and are better able to interact with and break apart the solute.

. This plot is based on the vant Hoff equation. Chemistry questions and answers. Dissolving a Substance in Different Liquids E.
The extent to which an organic compound likes being surrounded by liquid water is of utmost importance to the environmental behavior and impact of the compound. Discuss the roles of lattice- and hydration energy in determining the solubility of a salt in water. Stirring does not have an affect on solubility of a substance but everyone knows that if he puts sugar in his tea and does not stir it will not dissolve.
Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas. Stir the mixture well. Ionic solids or salts contain positive and negative ions.
Stirring increases the speed of dissolving. SOLUBILITY Size Matters Group 2. In Part IV and V of the experiment you observed the solubility of Ca 1032 in both water and KIO3.
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category Analytics. Chemistry questions and answers. Solubility may be determined according to the function of the study as follows.
Sorting Materials into Groups in Science for grade 6. In this section we will concentrate on solubility melting point and boiling point. 2What sort of additional interactions are taken into account when doing solubility calculations with activities as opposed to those calculated only using molarities.
11315 4 will plot changes in volume if any and explain their results by taking into account type of intermolecular forces. Place 1 cup of room temperature water into 3 containers. In terms of quantity solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given temperature.
Solubility is impaired by two direct factors. In the case of sugar and water this process works so well that up to 1800 grams of sucrose can dissolve in a liter of water. There are three factors that affect solubility.
You want to create the sweetest chocolate bar by maximizing the sugar concentration. Additionally two immiscible liquids will be used to perform a liquid-liquid extraction with the. Repeat the same with other liquids as many different liquids are available to you.
Solubility is the ability of a solid liquid or gaseous chemical substance or solute to dissolve in a solvent usually a liquid and form a homogenous solution. Solubility Miscibility Revised. Solubility is the overall volume of a material that can melt at a certain temperature in a specified amount of solvent.
Let it stand for five minutes. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The solubility of both solids and gases is affected by temperature but pressure only influences the solubility of gases.
Solubility may be determined at several temperatures and plotted against the reciprocal of the absolute temperature temperature in C 273 resulting in a straight line. Write the solubility product expression for a salt given its formula. Deviations from Henrys law are observed when a chemical reaction takes place between the gaseous solute and the solvent.
Actually if we left the tea to stand for a long enough time the sugar would dissolve. The solubility of a given solute in a given solvent typically depends on temperature. This chemical property is called the aqueous activity coefficient and it is closely related to the compounds aqueous solubility.
Stirring only increases the speed of the process - it. This factor affects the solubility of. The weak bonds that form between the solute and the solvent compensate for the energy needed to disrupt the structure of both the pure solute and the solvent.
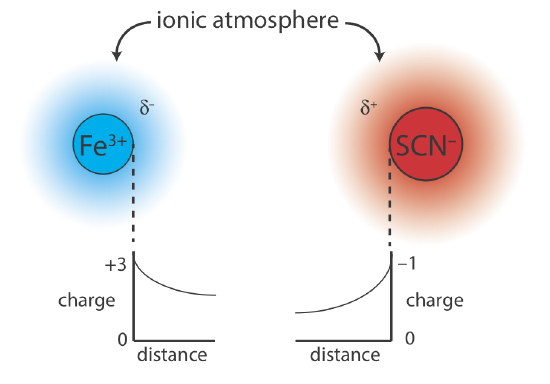
An understanding of bond dipoles and the various types of noncovalent intermolecular forces allows us to explain on a molecular level many observable physical properties of organic compounds. Based on the concept of activities and using Table 1 for this experiment in your lab manual how does activity explain the differences in the observed solubility of Ca 1032 into each of these solvents. AAs bBaqcCaq aA s bB aq cC aq is Ksp BbCc K sp B b C c.
Thus for example the solubility of ammonia in water does not increase as rapidly with increasing pressure as predicted by the law because ammonia being a base reacts to some extent with water to form ammonium ions and hydroxide ions. Up to 24 cash back solvent. Explain the distinction between an.
2 glasses with tap water Salt iodized salt and normal table salt Teaspoon timer. Explain the effect of particle size in solubility. Mass of water and solubility g salt 100 g solvent for all six trials.
1how does activity explain the differences in the observed solubility of Ca IO32 into each of these solvents. All the mixture to sit for a few minutes. Solubility products are useful in predicting whether a precipitate will form under specified conditions.
To determine whether a solute will dissolve in a solvent remember this saying. Solubility the amount of substance that can dissolve in a liquid is a physical property. Observe whether the liquid mixes with water or not.
Construct a solubility graph using the temperature and solubility information from the. Based on the concentration of solute dissolves in a solvent solutes are categorized into highly soluble. Explain what a qualitative analysis separation scheme is and how it works.
Making sure that the bulb of the thermometer does not touch the bottom the beaker or the ice when taking the temperature You are in a laboratory creating a new chocolate bar. Cookie Duration Description. The smaller the solubility product the lower the solubility.
Solubility is the new bond formation between the solute molecules and solvent molecules. Explain the activity to demonstrate the. After performing the activity the students shall be able to.
Does colored sugar dissolve equally well in water vegetable oil and. Based from your activity try to explain your results. Solubility is a property referring to the ability for a given substance the solute to dissolve in a solvent.
Explain the activity to demonstrate the solubility of liquids in water. For many solids dissolved in liquid water solubility tends to correspond with increasing temperature. The general form of the solubility product constant K sp for the equation.
Solubility is the amount of a solute needed to form a saturated solution at a specific temperature and specific solvent amount. Include a separate entry for the unknown solutions identification number characteristic temperature and concentration. Solubility as a Function of Temperature.
Add 14 tsp of salt sugar and flour into separate containers. In the coming activities you will learn more about dissolving solids and liquids and see that gases can dissolve too.
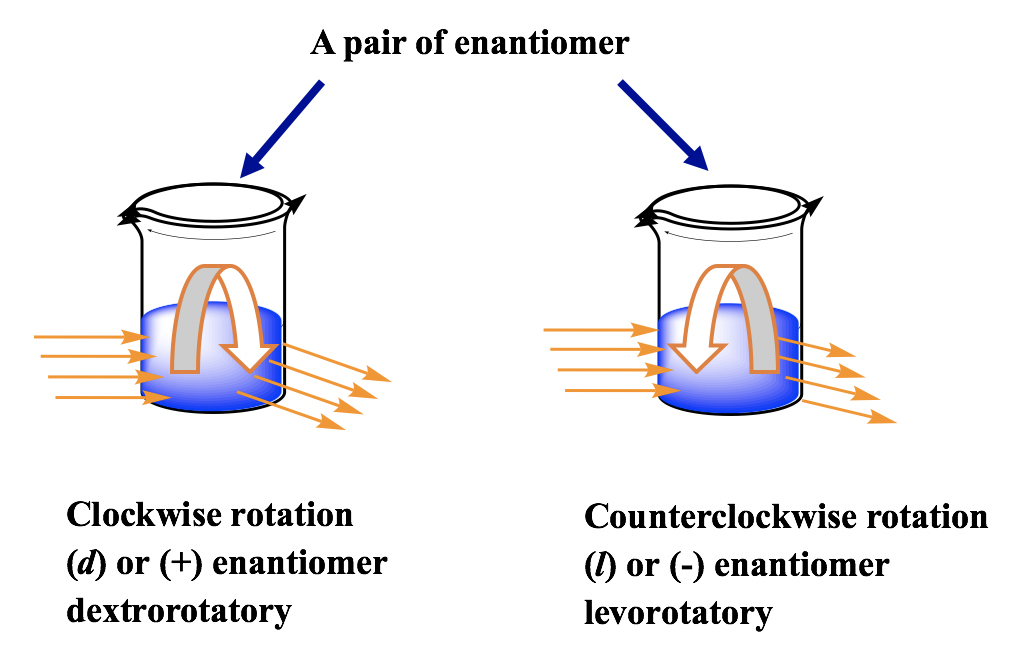
5 4 Optical Activity Organic Chemistry I
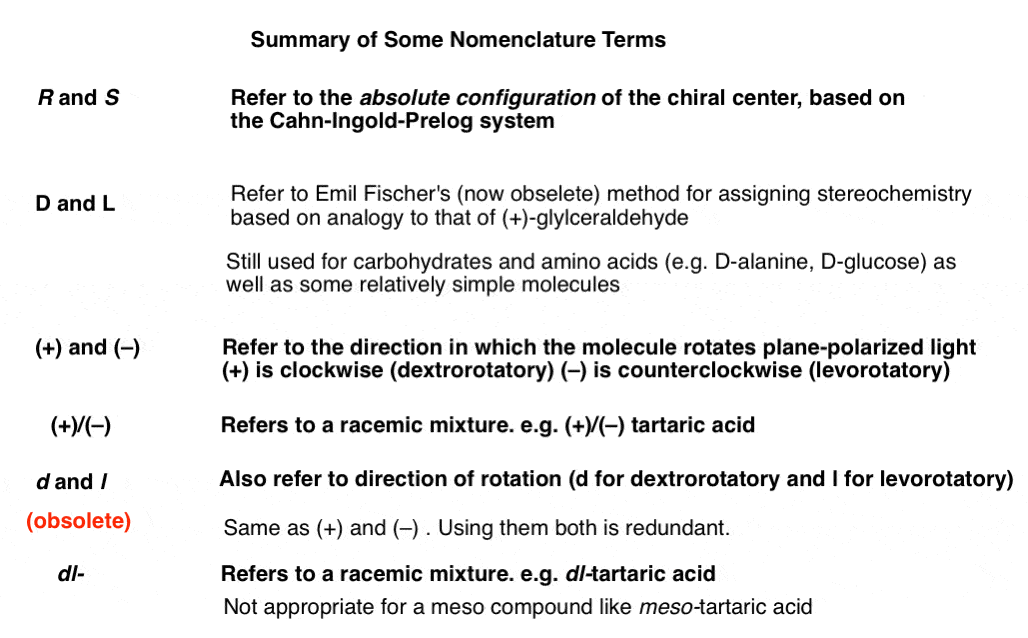
Optical Rotation Optical Activity And Specific Rotation

Activity Coefficient An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Activities And Their Effects On Equilibria Chemistry Libretexts
0 Response to "How Does Activity Explain the Differences in the Observed Solubility"
Post a Comment